Income from Business & Profession
Home » Income from Business & Profession
How Income from business and Profession is Treated under Income Tax?
Income from business and profession refers to the earnings of individuals or entities through commercial activities or professional services. Business income usually arises from selling goods or services with a profit, where the deducted expenses occur. Practitioners like doctors, lawyers, and consultants may be said to generate income through their specific services considering their acquired expertise. Business and professional income types are indispensable for the economy because they contribute to economic growth, job creation, and innovation. Knowledge of where each differs in taxation, regulations, and financial management is essential to proper management and earnings maximization.
What is Business?
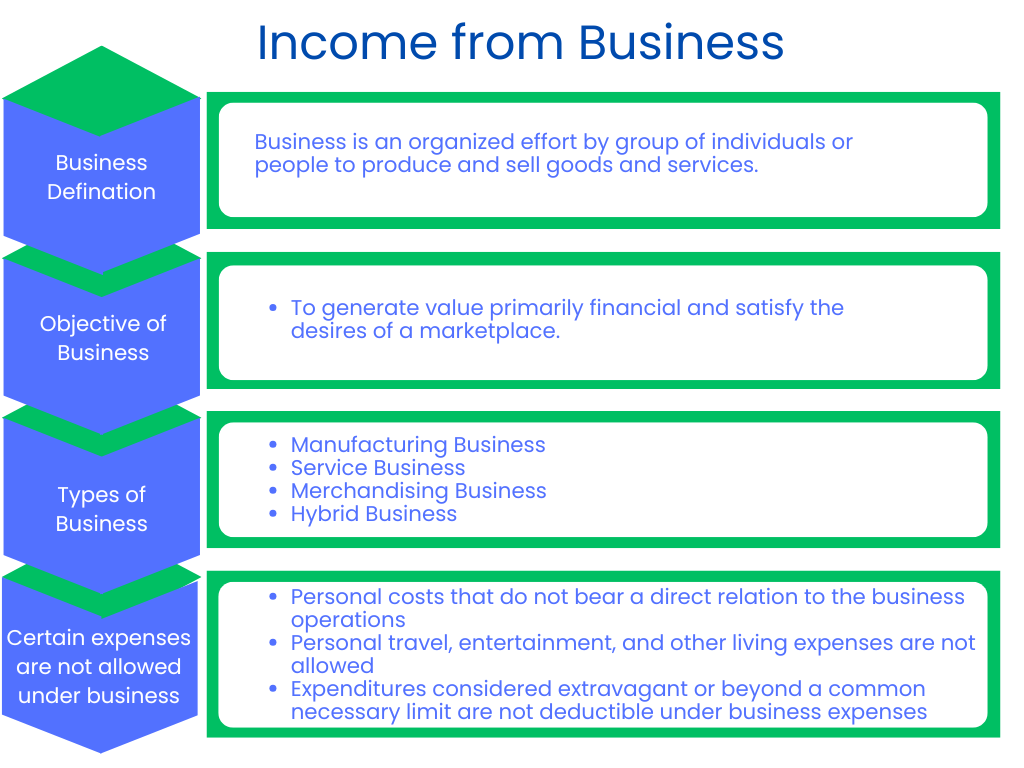
Business means organized efforts by people or groups of individuals to produce and sell goods and services in the quest for profit. The business consists of many activities to satisfy the wants of people, which will also provide financial returns to the owners or stakeholders. In any guise- a corner store or a large multinational business- It operates in sectors like technology, healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, among many others.
The most basic components of a business are producing goods or services, marketing, sales, and financial management. Effective companies are based on innovation, customer satisfaction, and efficient operations. Successful businesses mostly focus on creating value for their customers, providing good quality products or services, and building relationships with clients, employees, and suppliers.
Different models of businesses are available; the first model contains physical storefronts, while the second model purely relies on online sources. Key factors to a business’s successful longevity are responsiveness to change in the market, risk management, and taking available opportunities for such enterprise. Businesses must also observe laws and regulations, handle finances wisely, and maintain a good work culture to ensure continuous growth and sustainability. Simply put, business is a dynamic activity that promotes economic development and enhances the quality of life for individuals and society.
Objective of Business
The core goal of a business is to generate value – primarily financial – around the products or services that satisfy the desires of a marketplace. Beyond generating profits, businesses are also vital to the economy, offering employment, leading to innovation, and promoting economic development overall.
Types of Business
- Manufacturing Business: Manufactures products from raw materials.
- Service Business: Sells intangible products, such as consulting, health care, or financial services.
- Merchandising Business: Buys and sells goods in essentially a non-altered state, such as retailers who sell in a store.
- Hybrid Business: It combines manufacturing and service businesses, such as restaurants.
What is your Profession/Vocation?
A profession is an occupation that requires a high level of education, training, and expertise in a certain field. Unlike general employment, professions often entail higher skill and knowledge, thereby entailing ethical standards and codes of conduct. Professions are mostly governed by recognized organizations or regulatory bodies that ensure practitioners uphold competence, integrity, and ethical behavior.
Professions can include common ones such as law, medicine, engineering, accounting, teaching, or architecture. These professions often require qualifications, such as degrees or certifications, before one is allowed to legally and competently practice. For example, a doctor requires medical school along with the completion of licensing exams to practice, while a lawyer completes a law degree and also has to pass the bar to practice law.
Whereas a vocation is mostly understood as a calling or occupation that brings deep fulfillment and may or may not demand formal education, it is generally a form of work facilitated by passion, personal mission, or a sense of duty. All professions are forms of vocations; however, not all vocations are forms of professions. For instance, a teacher, a social worker, or an artist might consider his job as a calling if he is called to it personally, although this is not an association that is professionally governed.
Both professions and vocations play a vital role in society by providing services that enhance the quality of life, fill critical needs, promote knowledge, and spur innovations. Although a profession often places strong credentials at the forefront, a vocation often centers on personal values and satisfaction or gratification in work. Whatever the type, professions, and vocations are crucial components of the social and economic structure of any community.
Characteristics of a Profession
- Expert Knowledge: Rich in-depth training and skills.
- Service Orientation: Professions generally serve a need in society (such as healthcare).
- Ethics Requirements: Obeyed code of ethics to maintain their members’ trust.
- Licensure/Certification: Most professions need a license or certification before practice.

Business and Profession
- Objective – Business is operated in the quest for profit while the professional is for the provision of professional services.
- Regulation: Professions are self-regulatory and businesses are governed under the law of the market generally
- Risk: Businesses face entrepreneurial risks as professionals face risk in their professions
- Salary Income: These are incomes earned in employment, such as wages, gratuities, and other allowances. Salaries are subject to withholding tax and other deductions.
- Business Income: Profits arising from trade, manufacture, or any form of commercial activity. Business income taxes are paid on net earnings since revenue minus business expenses is the net income.
- Profession Income: These are income-earning based on personal expertise or services such as lawyers, doctors, or accountants. Professionals prepare taxes based on fees minus expenses that are allowed.
- Rental Income: Income generated from renting real estate or other rental assets. Most maintenance costs and other property-related taxes are tax deductions.
- Capital Gains: Profits arising from selling capital assets that include stocks, bonds, or other property. Short-term and long-term may be subjected to different taxes.
- Interest and Dividends: Income from bank deposits, bonds, or stocks. Although interest income from qualified stocks will be taxed at favorable rates, income from interest normally is considered regular income.
- Royalties: Payments for rights associated with intellectual property such as copyrights or patents. Royalties are normally considered ordinary income.
- Other Income: Income from sources such as lottery winnings, gifts, or pensions. The country depends and the treatments and tax rates may vary.
- Progressive Taxation: Most countries tax using a progressive system that allows the tax rate to increase with every rise in income. However, there may be different types of income that are taxed at specific rates or exempted.
Certain expenses are not allowed under Business and Profession.
Both professions and businesses have specific disallowed expense categories for tax purposes and business activities, which they are not allowed to claim. Typically, these disallowed expenses include personal costs that do not bear a direct nexus to the operational duties of the business or the practice of the profession. For example, personal travel, entertainment, or other living expenses unrelated to the work are generally not deductible. Also, fines or penalties imposed for legal infractions, such as traffic tickets or tax penalties, cannot be deducted as business expenses. In a medical or law profession, expenditures on gifts and personal articles for clients that are over an established limit may not be deductible. Expenditures considered extravagant or beyond what is commonly necessary to carry on the trade or business, such as expensive dinners or excessive office decorations, might be questioned and, therefore, disallowed by the tax authorities. Understanding these limitations helps people in tax compliance and savings, avoiding penalties for businesses and individuals alike.
Depreciation
What is Depreciation?
Depreciation is the systematic reduction of the recorded cost of any tangible asset over its life. It represents wear and tear, usage, or obsolescence and aids in correctly showing an asset’s value on financial statements.
The objective of Depreciation:
Cost Distribution: Assigns the cost of a long-term asset to the years the asset is in use.
Tax Credit: Depreciation is an allowable tax credit that reduces taxable income.
Effect of Depreciation on Taxes:
It reduces the value of an asset in books, and thus, decreases the taxable income of a business. Typically, businesses exercise it as an operating expense to decrease the taxable income. In case accelerated depreciation methods like double-declining balance are used, more deduction is reaped during the early years where businesses avoid paying taxes till later periods.
Other Deductions
Business and Professional Common Deductions
- Business Expenses: All the usual and necessary expenses to run a business, including rent, utilities, and office supplies.
- Employee Salaries and Benefits: Salaries and wages paid to employees, including bonuses, and benefits such as health insurance among others.
- Home Office Deduction: If you work from home, you might be in a position to declare some of the costs in terms of maintaining a dedicated workspace: part of rent or mortgage and utilities based on office space usage.
- Interest Expenses: Interest paid on business loans is normally deductible which reduces taxable income.
- Business-Related Travel and Meals: Traveling away from home for business, including lodging and meals qualifies, although there are limits on the amount that can be deducted. For example, on a meal expense, it can only deduct that percentage of the meal cost.
- Donations: Donations to qualifying charitable organizations qualify, but deductions are capped based on your income.
- Insurance Premiums: All premiums for policies of business-related insurance, such as liability, property, and workers’ compensation, are deductible.
- Advertising and Marketing: This encompasses all expenses run for the business, such as web page costs, advertising, and promotional materials. These are considered as deductions.
- Education and Training Costs: All kinds of continuing education or professional development that has to do with maintaining or improving job skills is a deductible expense.
- Amortisation of Intangible Assets: Intangible assets would include patents, goodwill, or licenses, and licenses could be amortized or amortized to reduce taxable income.
Conclusion
Understanding what financial planning is, at its core-it has to include understanding the essentials of business and profession and the nature of taxable incomes, depreciation, and other deductions-leverages depreciable items such as interest on loans and other business expenditures into the best tax strategy for a business or professional. Similarly, knowing the difference between income types contributes correctly to reporting and taxation, which in turn gives business enterprises and professionals long-term sustainability and growth.
Get Started with TaxDunia Today
TaxDunia offers resources, guides, and tools for tax filing, GST, accounting, and financial management. With expert guidance, TaxDunia aims to simplify financial complexities for optimal tax benefits. Reach out to us for services to meet compliances and liabilities.

