GST Returns
Home » GST Returns
GST Return Types & Filing Procedure
GST returns are the most vital compliance requirement that businesses are subjected to in India. The knowledge regarding the kinds of returns, the method for filing returns, and the people eligible to submit it along with the consequent penalties keeps you on the right side of the law and avoids unnecessarily paying fines. This is a detailed guide about the GST return process, submission of GST returns, and the aftermath of making timely submissions.
Types of GST returns
Return Type | Purpose | Frequency | Due Date |
GSTR-1 | Report outward supplies (sales) | Monthly/Quarterly | 11th of the following month |
GSTR-2A | Auto-generated details of inward supplies | Monthly | No specific due date |
GSTR-3B | Summary of outward and inward supplies, ITC claim | Monthly | 20th of the following month |
GSTR-9 | Annual return summarizing all transactions | Annually | 31st December of the following year |
GSTR-9C | Reconciliation statement between GSTR-9 and financials | Annually | Same as GSTR-9 |
GSTR-4 | For the composition scheme taxpayers | Quarterly | 18th of the month following the quarter |
GSTR-6 | For Input Service Distributors (ISDs) | Monthly | 13th of the following month |
GSTR-7 | For tax deductors reporting TDS | Monthly | 10th of the following month |
GSTR-8 | For e-commerce operators reporting TCS | Monthly | 10th of the following month |
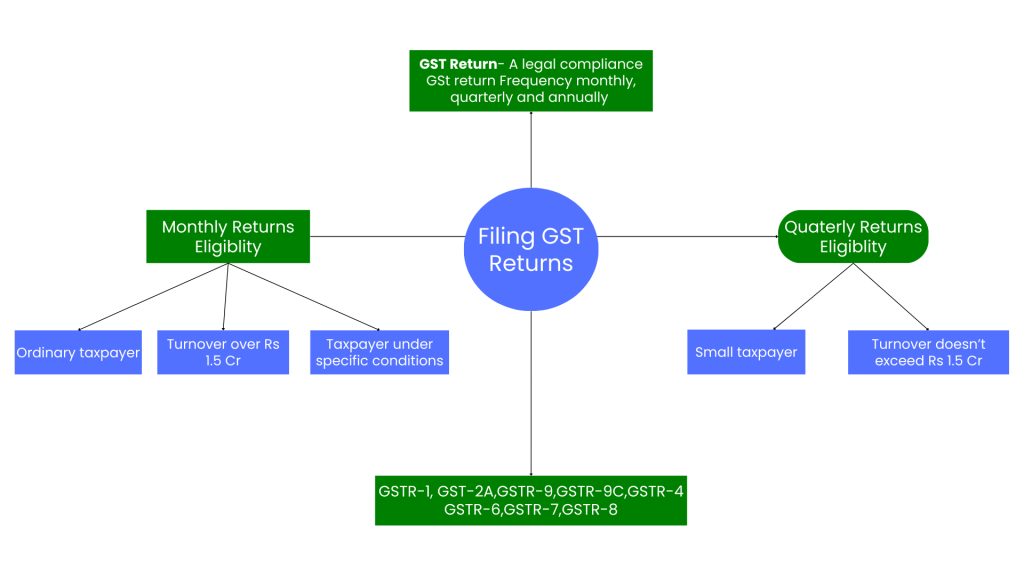
Monthly vs. quarterly returns: Eligibility and process
The most prominent compliance activity in any Indian business is GST returns. As taxpayers, it allows a person to make his or her GST returns every month or quarter based on their turnover and the kind of business they run. Concerning this eligibility, knowing the procedures also ensures ease of taxation by them.
Monthly Returns Eligibility
- Ordinary Taxpayers: If the total turnover during the last financial year is above INR 1.5 crores, then the returns are filed monthly.
- Taxpayers under Specific Conditions: Some categories of taxpayers, such as e-commerce operators or those making inter-state supplies, also file their returns every month, irrespective of the volume of their turnover.
Steps
- Obtaining Documents: Get photocopies of all the sales and purchase invoices related to outward and inward supplies.
- Matching Reconcile: Outward supplies match up with inward purchase data so that possible mismatches can be ruled out.
- File GSTR-1: It is a return indicating the supply made outside your organization. It needs to be filed by the end of the 11th of the previous month.
- File GSTR-3B: This summary return reflects both out and in supplies. Its return has to be filed till the 20th date of the following month.
- Pay the tax from the challan generated, through the GST portal.
- Prepare returns and preserve payment receipts for future usage.
Quarterly Returns
Eligibility
The following category of taxpayers shall be allowed to file a quarterly return under the QRMP-quarterly return monthly payment scheme if their aggregate annual turnover from all businesses horizontal and /or vertical doesn’t exceed 1.5 cr.
- Small taxpayer.
- Optional Quarterly Return: Taxpayers may still opt for quarterly returns even if the turnover exceeds the limit, provided they comply with the rules of the QRMP scheme.
Procedure
- Collect Quarterly Information: Collect all sales and purchase invoices throughout the quarter.
- Reconcile the Transactions: As in the case of monthly returns, data must be correct and uniform across the books.
- GSTR-1: Quarterly filers have to file GSTR-1 for the quarter by 11th of the following month.
- File GSTR-3B: Taxpayers may file GSTR-3B either monthly, that is, by the 20th of each month, or quarterly, that is, by the 22nd of the following month in case taxpayers have a turnover up to INR 5 crores.
- Tax Payments: In the case of quarterly GSTR-3B, the tax payable must be paid through the portal based on the frequency chosen.
- Books of Accounts: Maintain books of accounts and returns submitted for auditing and accountability.
Key Differences
Frequency: Monthly return needs more frequent reporting as against quarterly returns, which offers a longer period for collating data.
Turnover Threshold: Quarterly filing is optional for smaller businesses while monthly returns are required for greater turnover firms.
Filing Deadlines: Filing by returns and payments’ dates is different.
How to file GSTR-3B: A complete guide
Filing GSTR-3B is a much-needed compliance requirement for entities registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) in India. GSTR-3B is the summary return that collects data on both outward supplies, inward supplies, and the Input Tax Credit (ITC) claimed. For details on how to file GSTR-3B seamlessly, refer to this complete guide below.
GSTR-3B needs to be submitted by all registered taxpayers on a monthly basis, irrespective of their turnover. It is meant to return the tax liability for the month and allow for claiming the eligible input tax credit. The submission date of GSTR-3B is the 20th of the succeeding month.
Step-by-Step Procedure for Filing
Step 1: Open the GST Portal
- Go to GST Portal: [www.gst.gov.in] (http://www.gst.gov.in).
- Login: Enter using your login credentials- username and password. In case you are a first-time user, you have to create a login first.
Step 2: GSTR-3B Section
- Return Dashboard: Log into the website using the dashboard on the returns page followed by clicking “Return Dashboard”.
- Financial Year and Month: Then choose your financial year along with the month you wish to submit GSTR-3B for.
Step 3: Filling GSTR-3B Form
The GSTR-3B form is divided into several sections, which must be filled out carefully.
- Details of Outward Supplies:
Fill in the total value of outward supplies made during the month.
Categorize the sales based on applicable tax rates: 0%, 5%, 12%, 18%, and 28%.
Add any supplies that are exempt or non-GST.
- Input Tax Credit (ITC):
Eligible ITC: Report the ITC claimed on inward supplies against eligible purchases.
ITC Reversal: In case some ITC is not eligible or has been reversed, it should be reported in the respective columns.
The form contains different segments for reporting ITC on imports and input services.
- Tax Payable:
Calculate the total tax payable by subtracting the ITC on outward supplies.
The amount payable under each rate.
- Tax Payment:
When there is a tax to be paid, then there is a need to raise a challan for that amount of payment.
The payment medium to be chosen can be Internet banking, debit/credit card, or NEFT/RTGS
- Interest and Penalty:
If so, calculate and add any interest or late fee for delayed payments.
Step 4: Verification and Submissio
- Verification: Once submitted, check that all entries are accurate and there are no discrepancies in the sales information and ITC availed.
- Submit: Submit GSTR-3B; on successful submission, the system will display an acknowledgment receipt.
Step 5: Payment of Tax
If there is any tax liability, then pay as follows:
- Generate Challan: After submitting the return, generate a challan for the payable amount of tax.
- Make Payment: Make payment through the chosen mode and save the confirmation for future reference.
Step 6: Download Acknowledgment
1. Receipt of Acknowledgment: After submitting the GSTR-3B, obtain an acknowledgment receipt.
Due dates and penalties for late GST filing
Every business needs to follow up on the due dates when it comes to GST returns. The due dates for all types of GST return filings may vary. In case there is a delay in filing GST, there are related penalties and liabilities. It is as follows:
Due date of GST Returns
- GSTR-1
Purpose: This is the reporting for outward supplies or in general words sales.
Frequency: Quarterly (regular taxpayers) for QRMP Scheme Small Taxpayer Scheme
Date
- 11th of succeeding month if done monthly, it should be done once every month
- 11th of following month subsequent on completion of a quarterly; every three months after due quarter.
Due Date: 20th of the following month.
- GSTR-9
Purpose: Annual return summarizing all transactions of the financial year.
Frequency: Annually.
Due Date: 31st December of the following financial year.
- GSTR-9C
Purpose: Reconciliation statement between GSTR-9 and audited financial statements.
Frequency: Annually.
Due Date: Same as GSTR-9.
- GSTR-4
Purpose: For composition scheme taxpayers.
Frequency: Quarterly.
Due Date: 18th of the month following the quarter.
- GSTR-6
Objective: For Input Service Distributors.
Frequency: Monthly.
Due Date: 13th of the following month.
- GSTR-7
Objective: For tax deductors reporting TDS.
Frequency: Monthly.
Due Date: 10th of the following month.
- GSTR-8
Objective: For e-commerce operators reporting TCS.
Frequency: Monthly.
Due Date: 10th of the following month.
Late Filing Penalties
Late filing of GST returns attracts a series of penalties:
- Late Fees
GSTR-1: Rs 50 per day (Rs 20 for Nil Returns).
GSTR-3B: Rs 50 per day (Rs 20 for Nil Returns).
The late fee for all the returns is restricted to Rs 5,000.
- Late Interest on Payable Taxes
Interest is charged on any tax liability arising and not paid by the due date. The rate is normally 18% per annum, calculated on the amount due from the due date until the date of actual payment.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance
Cancellation of Registration: Failure to file returns consecutively for more than six months may attract cancellation of GST registration.
Legal Actions: Legal cases can be filed by tax authorities against habitual defaulters, which will again attract penalties under the GST Act.
How to avoid Late Filing Penalties?
- Advance Reminders: Set reminders a week in advance of due dates to ensure timely filing of returns.
- Seek Professionals: Engage a tax consultant or accounting software to track compliance requirements.
- Check the GST portal for dates and changes in compliance requirements.
Conclusion
It is thus crucial for businesses to stay updated about the various due dates for different GST returns and the penalties imposed in case of delay. On-time filing saves a business from penalties while also keeping the business operation smooth and enhancing credibility. Thus, proper record-keeping and effective filing processes would help businesses to navigate through the GST landscape.
Get Started with TaxDunia Today
TaxDunia is an all-inclusive tax and financial solutions platform designed to make finance management easier for individuals and businesses. TaxDunia Provides services like GST filing, income tax return filing, bookkeeping, compliance management, and tax advisory services. TaxDunia makes the experience seamless with expert guidance. It is customer-centric and offers reliable, timely support

