GST Penalties & Offenses
Home » GST Penalties and Offenses
GST Penalties and Offenses
Since the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system is becoming more and more intricate in India, there has to be an approach so that the tax may be correctly complied with. Hence this guide would point out the nature of types of penalties levied in GST, general offenses involved, their result, a strategy on how to take care of charges imposed upon interest, as well as the procedure on appeal before GST penalties.
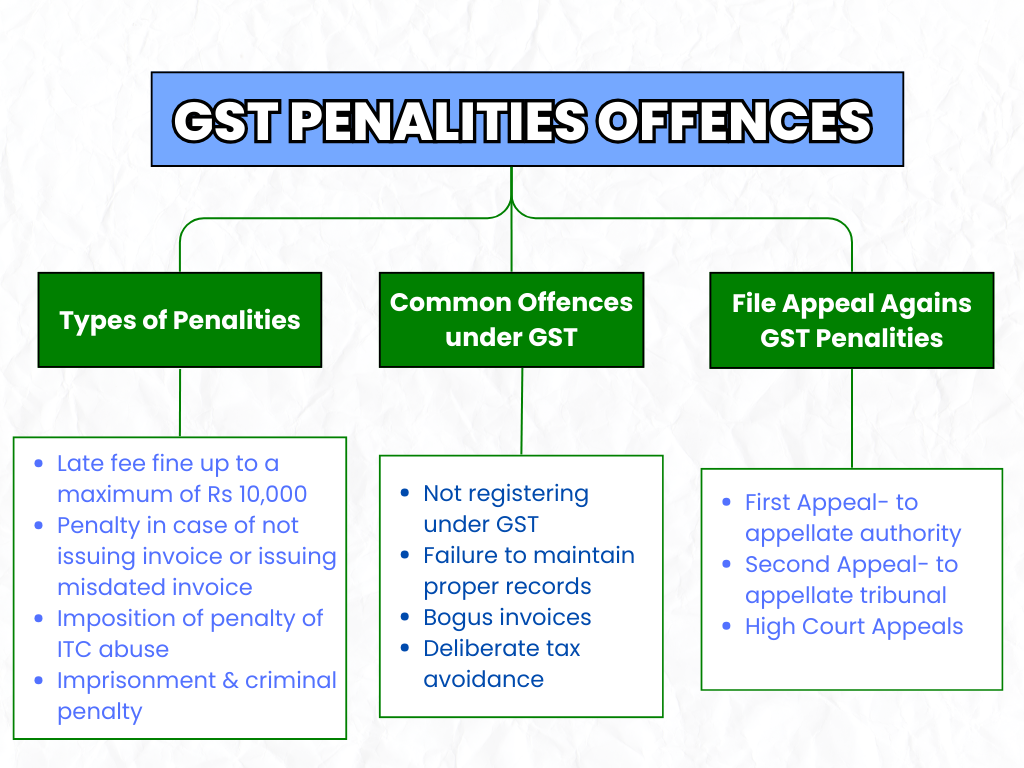
Types of Penalties Under GST & How They’re Calculated
Under GST, penalties are divided according to the nature and level of the offense. The first class has monetary fines, criminal prosecution, and imprisonment, which are the seriousness in sequence. The division of common penalties along with their calculation is shown below.
1) Late Fees and Interest on Delayed Payments
- Late Fees: If the GST returns are not filed by a taxpayer within the due date, he will be levied with late fees. For normal returns, say GSTR-3B, the fee is Rs 50 per day is Rs 25 each for CGST and SGST up to a maximum of Rs 10,000.
- Late Payment Interest: On late receipt of tax payments, interest of 18% per annum is payable. The interest is calculated from the day following the due date to the date of payment.
2) Underpayment of Tax Liability
- Amount of Penalty: In case, the tax amount shortfall has been due to the grounds of bona fide error or omission of accounting and returning the requisite details a penalty of 10% of the tax along with interest due is liable. And if the reasons are grounds of fraud then a penalty equivalent to an amount equal to 100% of the tax arrears along with Interest shall be charged.
- Computation: According to the case, in case of not issuing of invoice or issuing a misdated invoice, penalties are worked out based on the arithmetical amount of duty liability; each mistake is worked out with a different percentage:
3) Penalty in case of Not Issuing Invoice or Issuing Misdated Invoice
- Amount of Penalty: As an amount of not issuing of invoice or an error while issuing of invoice, it amounts to ₹10,000 or the amount of duty avoided, whichever is higher.
- Objective: This fine motivates the bookkeeping to be proper and, hence, the firms send out the invoices that are GST rule compliant.
4) Failure to Register
- Amount of Fine: As a case wherein a firm fails to register under GST when they should have, they face an amount of INR 10,000 or 10% of tax payable whichever is higher
- Importance: For the vigilance of a taxable business and for implementing the provisions for GST it is very much required to get themselves registered.
5) Imposition of Penalty for ITC Abuse
- Amount of Penalty: The penal amount in case of which business houses have misutilized their ITC includes interest at the rate of 18 percent and in addition to such interest also a penalty identical to the ITC amount of 100% if made in bad faith.
- Purpose: This is essentially a penal provision to deter this abuse of ITC, where it avoids revenue loss to the government.
6) Imprisonment and Criminal Penalties
- Reasons: For serious offenses such as false refund claims and tampering with books of accounts to evade tax, a person is imprisoned for up to 5 years along with another monetary penalty.
- Aggravation: For a higher amount of tax evasion of more than INR 5 crores and in case of repeated offenses, criminal liability applies.
Common Offences Under GST and Their Consequences
GST law puts several commonly committed offenses into different categories, with the imposition of punishments for each type. Offenses include procedure-based defaults as well as conscious avoidance attempts.
1) Not Registering under GST
- Offense: Those with supplies greater than 20 lakhs (special category states of 10 lakhs) in any State/Union territory are liable to get themselves registered under GST. Failure to obtain registration is an offense.
- Outcome: The business will face the consequences of being declared as an unregistered trader by the tax authorities and be subjected to penalties in the form of fines and confiscation of goods.
2) Willful Tax Avoidance
- Crime: Tax avoidance covers instances of false return submission, under-invoicing income, and exaggerating ITC.
- Outcome: Depending on the magnitude of the offense, they will face penalties, prosecution in court, and for cases of repeated large amounts of evasions, jail imprisonment.
3) Bogus Invoices
- Offense: Issuing fake invoices for collusive ITC or revenues is a serious offense.
- Consequence: Tax amount may attract a penal surcharge of 100% and, if not first time, also become liable for criminal prosecution.
4) Failure to Maintain Proper Records
- Offence: Commercial enterprises are expected to ensure they keep correct and comprehensive books of account which shall include invoices and ITC claims.
- Consequence: It will attract penalties and may make the claim ineligible at the time of assessment. Outcome: The organizations that refuse to allow GST authorities are subject to severe punishment and may even face imprisonment in case of reoffending.
How to Deal with GST Penalties and Interest Charges
GST penalties and interest charges must be dealt with the proper planning and understanding of the payment procedure. Some techniques for the same have been listed below:
a) Payment of Penalties Immediately
Procedure: Interest and penalty payments should be done through the GST portal. For smaller penalties, there is an option to make direct payments through the “Create Challan” facility.
Best Practice: Payment on time will avoid the addition of further interest. A separate provision for penalty and interest amount should be made in the financial plan.
b) Interest Recalculation and Adjustment
ITC Adjustment: In case of an ITC misreporting penalty, one can adjust entries for future tax periods, if so authorized by the GST authorities.
Interest Re-Calculation: As per GST law, interest is re-calculated when honest errors are involved. Here, corrections can be made with correct returns to reduce the interest liability.
end
c) Issuing Fake Invoices
Value: Complicated filing errors often lead to penalties, which tax professionals can avoid for clients. Tax consultants also assist businesses in penalty disputes.
Outcome: Professional advice increases accuracy, reduces the risk of penalty, and simplifies appeal against wrongful charges.
d) Correcting Errors in Returns
Self Correction: Errors that appeared in the filed returns are self-corrected in the subsequent month’s GSTR-3B or GSTR-1. Self-correction, of course, also means reduced chances of imposition of penalty. – Amendment Request: Serious errors noticed, affecting the ITCs or tax liability, and they can place amendment requests.
Filing an Appeal Against GST Penalties
The law mandates formal procedures for appealing if there is a dispute regarding GST penalties or an excessive imposition of the same that is considered unfair.
a) Procedure to Appeal
First Appeal: The appeal from the first instance needs to reach the Appellate Authority within three months from the date of passing the order. With an appeal, an amount of 10% of the tax amount in dispute needs to be deposited along with the appeal.
Appeal the Second Time: In case a person is not pleased with the decision given by the Appellate Authority, an appeal can be placed to the Appellate Tribunal.
High Court Appeals: Further appeal in higher courts is made if the legal grounds have their presence, mainly at places where substantial tax liability exists.
b) Documents Required:
Accompanying the appeal should be an affidavit, order in dispute copy, evidence of payment of penalty, relevant transaction records, etc.
Filing Process: An appeal under GST can be filed on the GST portal. The applicant needs to submit his case along with the justification of his case along with the transaction records.
c) Successful grounds for Appeals
Miscalculation of Tax: Where it is proved that a mistaken calculation and miscommunication is the cause of penalty but not an intention to evade tax.
Evidence of No Fictitious Intent: Corporate enterprises can show evidence that the corporation has acted responsibly with regard to its transactions; therefore, it is not required to pay penalties where an act of tax evasion is proved but no fictitious intent on the part of the defendant is established. There’s a greater likelihood that the appeal will be successful and such an appeal reflects no intention of tax fraud.
d) Response to Show Cause Notice
Notice Response: If an SCN is issued for penalties, then the business can plead its case to the GST officers before the SCN is eventually enforced.
Response in Time: The timely response to SCN along with all documents may help the business avoid proceeding with an appeal and can also reduce the penalty.
Conclusion
The GST system imposes penalties to ensure compliance, deter tax evasion, and encourage correct reporting. Understanding the type of penalties, common offenses, and how to handle and appeal penalties is important to businesses operating under GST. Proactive measures such as prompt payment of penalties, proper record-keeping, and professional tax advice can significantly mitigate risks.
This will provide an opportunity for the businesses that are penalized for fairly settling disputes. The businesses must maintain proper documentation and take prompt action regarding the notices to minimize disruption and cost.
Get Started with TaxDunia Today
TaxDunia is an all-inclusive tax and financial solutions platform designed to make finance management easier for individuals and businesses. TaxDunia Provides services like GST filing, income tax return filing, bookkeeping, compliance management, and tax advisory services. TaxDunia makes the experience seamless with expert guidance. It is customer-centric and offers reliable, timely support customized to the needs of every client. Choosing TaxDunia means convenience, accuracy, and peace of mind for all your financial and tax requirements.

