Partnership Firm/LLP Return
Home » Partnership Firm/LLP Return
Understanding Partnership Firms and LLPs: Filing Income Tax Returns (ITR)
In India, various legal structures are available for businesses to choose from. Partnership firms and Limited Liability Partnerships are the most common forms of these entities among small to medium-sized businesses because they are simple, flexible, and offer many liability protection benefits. Again, like any other business, both partnership firms and LLPs must adhere to the country’s tax laws, including the filing of ITR.
This article shall discuss the fundamentals of ITR filing for partnership firms and LLPs, which will include the process, relevant sections, due dates, and other important compliance aspects.
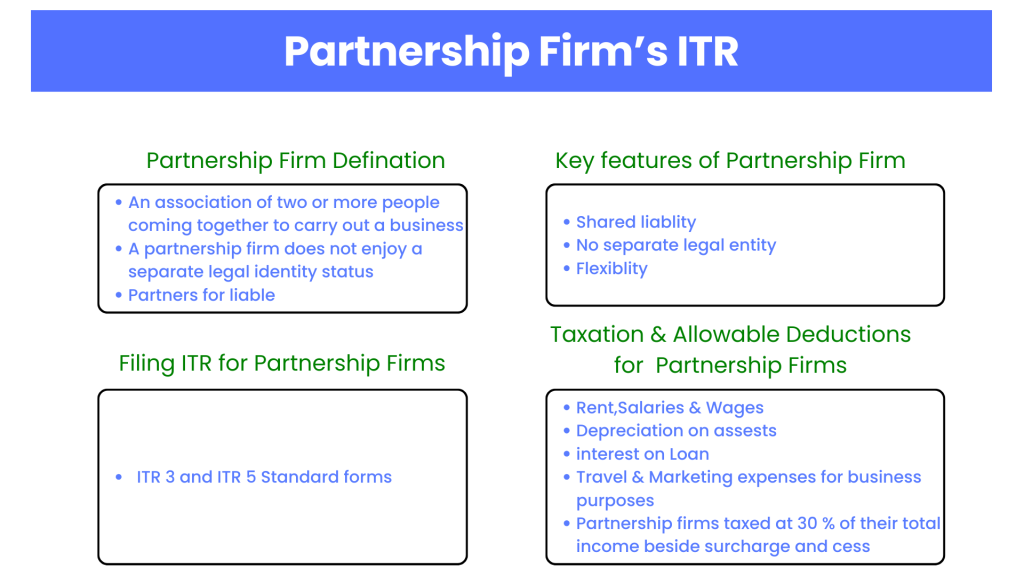
What is a Partnership Firm?
A partnership firm is an association of two or more people with the intention of carrying on a business for profit. Under the Indian Partnership Act, of 1932, both the profits and liabilities of the firm are shared by partners. A partnership does not have a legal identity like a company; its actions and liabilities are directly associated with those of the partners. This is the most popular format with professionals who may be lawyers, accountants, or even consultants.
Key Features of a Partnership Firm:
- Shared Liability: All the partners in a partnership are liable to pay the debt of the firm jointly and severally.
- No Separate Legal Entity: It is not considered a separate legal entity. It is directly connected to the partners.
- Flexibility: Management and business operations in a partnership firm offer flexibility.
What is an LLP?
A Limited Liability Partnership (LLP) is a hybrid structure that combines the best features of a partnership and a company. Like a partnership, it is formed by two or more individuals or entities, but it also provides limited liability protection to the partners. This means that in an LLP, partners are not personally liable for the firm’s debts beyond their agreed contributions to the LLP.
Key Features of an LLP
- Limited Liability: Partners are exempted from personal liability beyond their capital contribution.
- Separate Legal Entity: An LLP is considered a separate legal entity, hence, can own property, sue, or be sued as an independent identity of its partners.
- Flexibility: An LLP gives flexible management with fewer formalities in the matter of regulation than a company.

Filing ITR for Partnership Firms
A partnership firm will submit its income tax return as specified in Section 44AD, 44ADA, or section 44AE of the Income Tax Act as relevant to the nature and type of business undertaken. Typically, ITR-3 and ITR-5 are the forms that most partnership firms use.
Pre-filing Process of Partnership Firms
In general, the process for filing an ITR for a partnership firm involves the following stages:
- Choice of Correct ITR Form: A firm, being a partnership concern, must file ITR-5. It is specifically designed for firms and LLPs, and even for AOPs and BOIs. However, if the partners of a firm are individually filing their returns, then they would use ITR-3.
- Gather all required documents: The firm would require detailed financial records including balance sheets, profit and loss accounts, and a copy of the partnership deed when filing ITR-5. These records shall be required for the computation of tax. The firm shall have a record of its tax payments such as advance tax payments, TDS certificates, and other relevant documentation.
- The income of a partnership firm is calculated simply by summing all of the business profits accruing from revenue, capital gains, income from other sources, etc. It is then distributed to partners along with their share within it and handed over by them for tax returns in their returns.
- Set Off Losses: Any business losses incurred by the partnership firm can generally be carried forward and set off against profit earned during subsequent years.
File the Return: Once all the details are filled in, the return is filed online with the e-filing portal of the Income Tax Department. For return verification, firms also need to use a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC) or Aadhaar-based OTP for authentication.
Taxation and Deductions for Partnership Firms
Partnership firms are taxed at a rate of 30% of their total income as applicable besides surcharge and cess. Allowable deductions against partnership firms include those which are incurred directly for running the business, these include:
- Rent, Salaries, and wages
- Depreciation on assets
- Interest on loan
- Travel and marketing expenses on business proposal
In addition, if the turnover of the partnership firm is below Rs. 2 crores, the firm can choose a presumptive taxation scheme under Section 44AD and claim a fixed percentage (usually 8% of the total turnover) as the presumptive income for taxation purposes.
Preparation of ITR for LLP
LLPs, just like partnership firms, file income tax returns. The process of ITR filing for LLPs is similar to that of a partnership firm but with several differences.
Filing Process LLPs
A memorandum partnership firm, and other business entities too, use the same form, ITR-5, to file their returns. It captures the essential aspects of the financial performance of an LLP and other relevant tax information for presentation to the concerned tax authority.
Maintain Financial Records: LLPs must maintain detailed records of their financial transactions, including balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements, to accurately report their income and expenses. These records are used to calculate the LLP’s taxable income.
Consequently, it calculates its taxable income just like a partnership firm by adding and then subtracting the revenues raised from its business activities, investments, or other sources. The LLP’s tax-free liabilities are deducted in computing the taxable income.
Deductions for LLPs
LLPs are also entitled to claim deductions of business expenses, like salaries, office rent, depreciation, and professional fees. Similar to a partnership firm, LLPs can also avail of the presumptive taxation scheme under Section 44ADA if gross receipts do not exceed Rs. 50 lakhs.
E-filing and Authentication: After the preparation of an ITR, the return is e-filed on the Income Tax Department’s website. Verification of Return The LLP has also to authenticate the return by way of a Digital Signature Certificate (DSC).
Taxation and Deductions for LLPs
Though LLPs are taxed like partnership firms, at a base rate of 30% on total income, since LLPs are identified as separate entities in law, they are liable for taxation independent of their partners. All income distributed to partners is, therefore, nontaxable at the firm level. However, it gets taxed in the hands of individual partners when they file their returns.
Like partnership firms, LLPs are eligible for the following tax deductions:
- Depreciation on assets used in the business
- Interest on loans
- Salaries and wages paid to employees
- LLPs are also eligible under Section 44ADA presumptive taxation, which allows a fixed percentage of income to be declared without going into complete bookkeeping of accounts. This is more useful in small LLPs involved in professional services such as legal, consultancy, and accountancy services.
Due Dates for ITR Filing
Filing income tax returns is a statutory compliance requirement for all partnership firms and LLPs. The ITR filing due date falls under the following general guidelines:
For Firms and LLPs: the due date for filing ITR by the partnership firm or LLP is October 31st of the assessment year, if the accounts are not to be audited; if these accounts are required to be audited the deadline will be November 30th of the applicable year.
Audit Needs: The entity needs to get its accounts audited by a qualified Chartered Accountant if the firm’s or LLP’s turnover exceeds Rs. 1 crore as well as Rs. 50 lakhs if it’s that of professionals. The return filed should be audited, which should be filed by November 30.
Extended Due Dates: The Income Tax Department will also extend the due date in certain cases mostly related to firms and LLPs which are complex or lengthy to audit.
In addition, it is essential to file by these dates to avoid penalties and interest for late filing. Penalty for the delay in filing can go up to Rs 5,000 under Section 234F of the Income Tax Act.
Compliance and Penalty for Non-Filing
Failure to file an ITR can attract several consequences in both partnership firms and LLPs. Besides the penalties levied for belated filing, non-filing can attract legal consequences where it might lead to tax audits or scrutiny by the Income Tax Department and also avert certain tax benefits such as carry-forward losses.
The Income Tax Department may levy a penalty for failure to file returns, up to as low as Rs. 1,000 or as high as Rs. 5,000, depending upon the delay, and the punishments may be more severe in case of serious offenses.
Conclusion
Filing ITR for partnership firms and LLPs is an integral part of business compliance. The process, though a routine one for small businesses, is very intricate and requires detail-oriented attention, especially in selecting the appropriate ITR form, proper management of financial records, and timely submission of returns. If followed appropriately, partnership firms and LLPs can fulfill their tax obligations, and benefit from tax deductions, exemptions, and the presumptive taxation scheme. Compliance with tax laws ensures that operations stay normal and devoid of unnecessary penalties so that emphasis is kept on growth and profitability.
Get Started with TaxDunia Today
To get the best-optimized services, reach out to TaxDunia. We have a dedicated team of professionals to address your grievances related to taxation. You work on establishing your firm while TaxDunia is backing you with doing all the legal work and drawing a strategic roadmap for your business’s growth.


